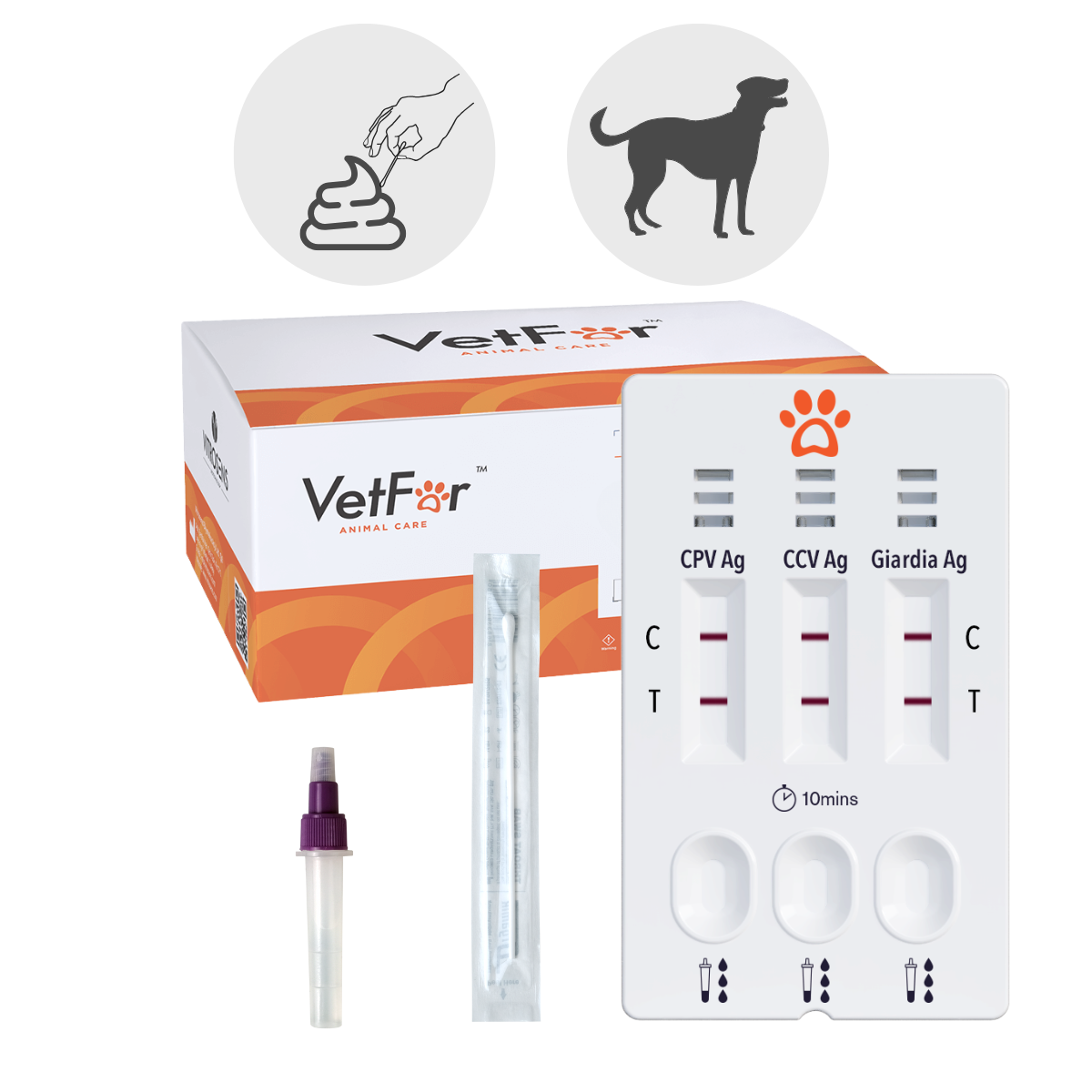
Canine Parvovirus (CPV) + Coronavirus (CCV) + Giardien Antigen Combo Test
The VetFor™ CPV + CCV + Giardia Combo Rapid Test enables the rapid and differentiated detection of canine parvovirus (CPV), canine coronavirus (CCV) and Giardia duodenalis in dog faecal samples.
48,00 €
| Quantity | Price | Discount |
|---|---|---|
| 3-5 | 46,56 € | 3% |
| 6-9 | 45,12 € | 6% |
| 10+ | 43,20 € | 10% |
| Sample type |
Faeces |
|---|---|
| Target specie |
Canine (Dog) |
| Target |
Canine Coronavirus (CCV) ,Canine Parvovirus (CPV) ,Giardia (Dog & Cat) |
| Packaging unit |
5 Tests |
The VetFor™ CPV + CCV + Giardia Antigen Combo Rapid Test is a veterinary in vitro diagnostic test for the differential and simultaneous detection of canine parvovirus (CPV), canine coronavirus (CCV) and Giardia duodenalis antigens in canine fecal samples. The test is based on the principle of the lateral sandwich immunoassay and enables rapid, precise diagnosis directly on site. The ready-to-use kit contains all the necessary components and is intended exclusively for use by veterinary professionals.
Product details
- Test type: Lateral sandwich immunoassay
- Target pathogens: Canine parvovirus (CPV), canine coronavirus (CCV), Giardia duodenalis
- Sample material: Fresh fecal samples from dogs
- Result time: Rapid test with direct evaluation within 10 minutes
- Detection limit: 5 × 10³ TCID₅₀ / mL
- Storage conditions: 2 – 30 °C
- Cross-reactions: No cross-reactions with CDV, ICH, PI2 or other common enteric pathogens detected
Performance data
CPV
-
Sensitivity: 98,15 %
-
Specificity: 100,0 %
-
Accuracy: 99,12 %
CCV
-
Sensitivity: 98,00 %
-
Specificity: 100,0 %
-
Accuracy: 99,08 %
Giardien
-
Sensitivity: 98,00 %
-
Specificity: 100,0 %
-
Accuracy: 98,90 %
Content
- 5 test cassettes (1 test per bag)
- 5 disposable bottles with dilution solution
- 5 sterile disposable sample swabs
- 5 sample swabs
- 1 instruction manual
For professional use only!
SHELF LIFE AND STORAGE
- The test kit must be stored at a temperature between 2 °C and 30 °C and a relative humidity of 40% to 60%. All components must be brought to room temperature before testing.
- Do not open sealed pouches and test kits until immediately before use.
- The test is stable until the expiration date. Do not use the test kit after the expiration date. The expiration date is indicated on the label/packaging of the sealed foil pouch.
- Do not expose the test kit to direct sunlight.
NOTES
- For in vitro diagnostic use only.
- For optimal test results, the manufacturer's instructions should be followed precisely.
- The tests should be conducted in compliance with biosafety measures and with protective clothing.
- The test kits must be kept in their sealed packaging until use.
- Do not use the test kit if the pouch is damaged or the seal is broken.
- The components of the test kit must not be reused.
- All components must be brought to room temperature before testing.
- The test kit may only be used up to the indicated expiration date.
- The components of this test kit have been tested as a standard batch.
- Do not exchange or mix components from different test kits.
- Do not touch the uncovered areas of the membrane in the test cassette.
- Inadequate or incorrect sample collection as well as improper storage and transport conditions may falsify the test results.
- All components of the test kit should be disposed of as infectious material.
You must be logged in to post a review.
Expert Knowledge on Giardia in Dogs and Cats
Giardia are single-celled parasites that infect the small intestine of dogs and cats, causing a disease known as giardiasis. The main causative agent is Giardia intestinalis (also called Giardia duodenalis), a flagellate that can infect both animals and humans.
Transmission and Epidemiology
Giardia transmission occurs primarily through the ingestion of cysts found in contaminated water, food, or on polluted surfaces. These cysts are resilient and can survive in the environment for several months. Dogs and cats often become infected by drinking from puddles, ponds, or licking contaminated areas. Giardia can also be transmitted between different animal species, with certain genotypes capable of infecting both animals and humans.
Symptoms
Infected animals often exhibit symptoms such as recurrent, pale, slimy, and foul-smelling diarrhea; in some cases, it may also be bloody. Vomiting, abdominal pain, bloating, weight loss, weakness, and fever are also common signs. However, it is important to note that not all infected animals show symptoms; some may remain asymptomatic, making diagnosis more difficult.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is usually made by examining stool samples, where cysts or trophozoites of Giardia can be microscopically detected. Molecular tests such as PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) can also be used to detect the parasite's genetic material in the stool. Since cyst shedding is not always constant, repeated tests over several days are required to diagnose the infection reliably.
Treatment
Treatment generally involves antiparasitic medications such as fenbendazole or metronidazole, which kill the Giardia. It is equally important to thoroughly clean and disinfect the environment to prevent reinfection, as the cysts can survive in the environment for several months. Especially in puppies and young animals, the symptoms can be more severe, so quick and consistent treatment is essential.
Prevention
Preventive measures include avoiding access to potentially contaminated water, regularly cleaning food and water bowls, and, if necessary, regular deworming and parasite control. Dogs and cats should be kept away from potentially infected animals, and in households with multiple pets, regular testing for Giardia should be conducted to prevent spread.
References
- Deutsche Familienversicherung. Giardiasis - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment. Retrieved from https://www.deutsche-familienversicherung.de/tierkrankenversicherung/hundekrankenversicherung/ratgeber/artikel/giardien-ursachen-symptome-behandlung/
- Zooplus. Giardia in Cats: Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention. Retrieved from https://www.zooplus.de/magazin/katze/katzengesundheit-pflege/giardien-bei-katzen
- Tierklinik Ismaning. Giardia in Dogs & Cats. Retrieved from https://www.tierklinik-ismaning.de/giardien-bei-hund-katze/
- Canikur. Recognizing and Correctly Treating Giardia in Dogs. Retrieved from https://www.canikur.de/was-sind-giardien
- AniCura Germany. Giardia in Cats, Diarrhea, Intestinal Parasite. Retrieved from https://www.anicura.de/fuer-tierbesitzer/katze/wissensbank/giardien-bei-katzen/
- Fressnapf. Giardia in Dogs: Infection, Symptoms & Treatment. Retrieved from https://www.fressnapf.ch/de/magazin/hund/gesundheit/giardien/
- Royal Canin. Giardia Infection in Dogs - Vet Focus. Retrieved from https://vetfocus.royalcanin.com/de/wissenschaft/giardien-infektion-bei-hunden
- Wikipedia. Giardiasis. Retrieved from https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Giardiasis
- Wikipedia. Giardia intestinalis. Retrieved from https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Giardia_intestinalis
Background on Canine Parvovirus (CPV)
Canine parvovirus (CPV) is a highly infectious pathogen that primarily affects the gastrointestinal tract of dogs. The virus belongs to the family Parvoviridae and is an unenveloped single-stranded DNA virus. Due to its high environmental resistance, it can survive in the environment for months and is mainly transmitted via the fecal-oral route. Unvaccinated puppies between four and twelve weeks of age are particularly susceptible to infection.
Disease Course and Symptoms
The incubation period is usually 3 to 7 days, after which clinical symptoms appear. Typical signs of CPV infection include severe vomiting, bloody diarrhea, fever, loss of appetite, and lethargy. The disease can be fatal within a few days, especially if early treatment is not provided. Dogs with weakened immune systems, as well as young puppies without sufficient vaccination protection, are particularly affected.
Recent Developments
In recent years, new CPV variants (CPV-2a, CPV-2b, and CPV-2c) have been identified, which differ slightly in their pathogenicity. Studies show that CPV-2c is increasingly widespread globally and may exhibit increased virulence. There is also evidence suggesting that some of these variants can infect cats, broadening the zoonotic significance of CPV.
Prevention
Vaccination is the most effective protective measure against canine parvovirus. The Standing Committee on Vaccination in Veterinary Medicine (StIKo Vet) recommends primary immunization for puppies at 8, 12, and 16 weeks, followed by a booster vaccination after 15 months. Subsequent vaccinations should occur every three years to ensure long-term protection.
In addition, hygienic measures are critical to controlling the spread of the virus. In households with a CPV infection, contaminated surfaces should be thoroughly cleaned with virucidal disinfectants, as conventional cleaning agents are often ineffective against the resilient virus.
References
-
Standing Committee on Vaccination in Veterinary Medicine (StIKo Vet) at the Friedrich Loeffler Institute (2022). Guidelines for the Vaccination of Small Animals, 5th Edition. Available at: https://www.openagrar.de/servlets/MCRFileNodeServlet/openagrar_derivate_00044276/Impfleitlinie-Kleintiere_2022-01-01_ba.pdf
-
Decaro, N., & Buonavoglia, C. (2012). Canine parvovirus—A review of epidemiological and diagnostic aspects, with emphasis on type 2c. Veterinary Microbiology, 155(1), 1-12. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.09.007
-
Pérez, R., et al. (2012). Evidence of a new canine parvovirus variant in dogs in Uruguay. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 50(11), 4146-4151. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01827-12
-
Mylonakis, M. E., et al. (2016). Canine parvoviral enteritis: An update on the clinical diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of the disease. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 30(3), 647-655. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/jvim.14192
-
Parrish, C. R., et al. (2013). Dogs are considered a reservoir for parvovirus. Veterinary Research, 44(1), 1-12. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/1297-9716-44-36
Translated from German version



Reviews
Clear filtersThere are no reviews yet.